Linux TASK_IO_ACCOUNTING功能以及如何使用
透过lxr的代码确认,在Linux 2.6.20以后引入了TASK_IO_ACCOUNTING功能,通过把每个线程和进程的io活动通过/proc/pid/io导出大大方便了用户,这里需要注意的是RHEL 5U4基于2.6.18内核但是他们backport了这个功能,并由此催生了相应的了解per进程Io活动的工具如pidstat和iotop, 这两个软件工作的时候截图如下:
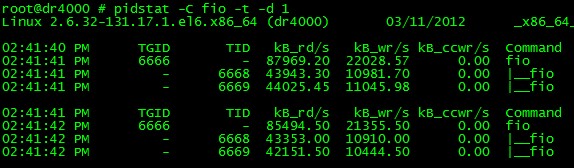
pidstat可以看到带层次线程IO活动
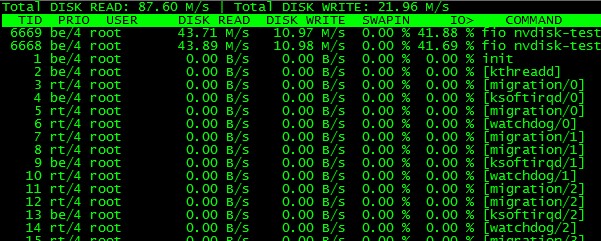
iotop能看到扁平线程IO活动
通过strace来了解到这二个软件关于IO活动部分输入源都是/proc/pid/io, 让我们来了解下这个文件:
# cat /proc/self/io rchar: 1956 wchar: 0 syscr: 7 syscw: 0 read_bytes: 0 write_bytes: 0 cancelled_write_bytes: 0
这个文件后三个参数是IO记账功能新添加的,我们来了解下他们的意义,摘抄从man pidstat:
kB_rd/s
Number of kilobytes the task has caused to be read from disk per second.
kB_wr/s
Number of kilobytes the task has caused, or shall cause to be written to disk per second.
kB_ccwr/s
Number of kilobytes whose writing to disk has been cancelled by the task. This may occur when the task truncates some dirty page-
cache. In this case, some IO which another task has been accounted for will not be happening.
接着我们再来看下内核如何统计这三个值的,在RHEL 5U4源码数下简单的grep下:
[linux-2.6.18.x86_64]$ grep -rin task_io_account_ . ./block/ll_rw_blk.c:3286: task_io_account_read(bio->bi_size); ./include/linux/task_io_accounting_ops.h:8:static inline void task_io_account_read(size_t bytes) ./include/linux/task_io_accounting_ops.h:13:static inline void task_io_account_write(size_t bytes) ./include/linux/task_io_accounting_ops.h:18:static inline void task_io_account_cancelled_write(size_t bytes) ./include/linux/task_io_accounting_ops.h:30:static inline void task_io_account_read(size_t bytes) ./include/linux/task_io_accounting_ops.h:34:static inline void task_io_account_write(size_t bytes) ./include/linux/task_io_accounting_ops.h:38:static inline void task_io_account_cancelled_write(size_t bytes) ./fs/direct-io.c:671: task_io_account_write(len); ./fs/cifs/file.c:2221: task_io_account_read(bytes_read); ./fs/buffer.c:965: task_io_account_write(PAGE_CACHE_SIZE); ./fs/buffer.c:3400: task_io_account_cancelled_write(PAGE_CACHE_SIZE); ./mm/truncate.c:47: task_io_account_cancelled_write(PAGE_CACHE_SIZE); ./mm/page-writeback.c:649: task_io_account_write(PAGE_CACHE_SIZE); ./mm/readahead.c:180: task_io_account_read(PAGE_CACHE_SIZE);
可以看出统计力度还是比较粗的。
同时Io记账相关的proc导出位于 fs/proc/base.c:
#ifdef CONFIG_TASK_IO_ACCOUNTING
static int do_io_accounting(struct task_struct *task, char *buffer, int whole)
{
...
return sprintf(buffer,
"rchar: %llu\\n"
"wchar: %llu\\n"
"syscr: %llu\\n"
"syscw: %llu\\n"
"read_bytes: %llu\\n"
"write_bytes: %llu\\n"
"cancelled_write_bytes: %llu\\n",
rchar, wchar, syscr, syscw,
ioac.read_bytes, ioac.write_bytes,
ioac.cancelled_write_bytes);
}
简单的分析了下TASK_IO_ACCOUNTING运作方式,对了解每个进程的IO活动还是很有帮助的。另外再罗嗦下在RHEL 5U4是可以用这个功能的。
建议继续学习:
- 通过『iostat -dx 1』命令监控IO性能 (阅读:4800)
- disktop per设备per应用层面的IO读写统计 (阅读:2572)
- Iostat看不到设备统计信息的原因分析 (阅读:1935)
扫一扫订阅我的微信号:IT技术博客大学习
- 作者:Yu Feng 来源: Erlang非业余研究
- 标签: iostat TASK_IO_ACCOUNTI
- 发布时间:2012-03-11 22:09:56
-
 [897] WordPress插件开发 -- 在插件使用
[897] WordPress插件开发 -- 在插件使用 -
 [135] 解决 nginx 反向代理网页首尾出现神秘字
[135] 解决 nginx 反向代理网页首尾出现神秘字 -
 [56] 整理了一份招PHP高级工程师的面试题
[56] 整理了一份招PHP高级工程师的面试题 -
 [54] Innodb分表太多或者表分区太多,会导致内
[54] Innodb分表太多或者表分区太多,会导致内 -
 [53] 如何保证一个程序在单台服务器上只有唯一实例(
[53] 如何保证一个程序在单台服务器上只有唯一实例( -
 [52] 全站换域名时利用nginx和javascri
[52] 全站换域名时利用nginx和javascri -
 [52] 分享一个JQUERY颜色选择插件
[52] 分享一个JQUERY颜色选择插件 -
 [52] 用 Jquery 模拟 select
[52] 用 Jquery 模拟 select -
 [52] CloudSMS:免费匿名的云短信
[52] CloudSMS:免费匿名的云短信 -
 [52] 海量小文件存储
[52] 海量小文件存储